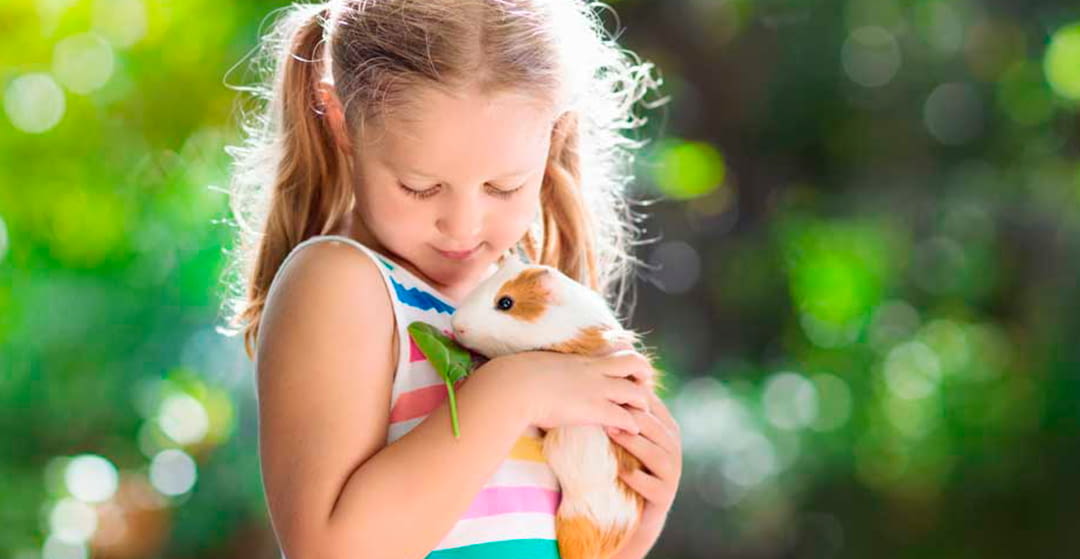
Rodents, such as hamsters or guinea pigs, are often considered ideal pets, especially for children and those new to pet ownership, thanks to their compact size and, for the most part, simple care requirements.
Other reasons make them the ideal pet, such as their low cost and maintenance or the lower risk of allergies since, compared to some furry pets, such as dogs and cats, rodents can be a safer option for people with this risk, since They tend to have less hair and dandruff.
Rodents stand out for their remarkable intelligence and affection. These adorable creatures do not demand large spaces, generate little noise, and generally do not require special care. Opting to adopt a rodent is presented as the ideal choice for those who want to escape the perpetual dilemma between dogs and cats. However, it is essential to know which rodents are most suitable as pets and make decisions based on the specific needs of each case.
In the absence of the definitive list, what will be the permitted companion animals that the Scientific and Technical Committee for the Protection and Rights of Animals must draft to include in the new animal welfare law, which would be developed within a maximum period of three and four years, and will be organized into lists of mammals, reptiles, birds, amphibians, fish and invertebrates. These are the most common rodents in our homes.
HAMSTER
Hamsters are small animals, generally ranging in length from 12 to 17 cm. They have soft fur and a short, thick tail. Their appearance can vary depending on the species, since there are various breeds of hamsters, such as the Syrian hamster and the Russian dwarf hamster.

Nocturnal:
Hamsters are nocturnal animals, meaning they are most active at night. This is important to keep in mind when planning interactions and activities with your pet.
Loners:
Unlike some other rodents, most hamsters are solitary animals and prefer to live alone in their cages. If they are kept together, especially if they are of opposite sexes, they may fight.
Habitat:
They need a suitable habitat that includes a cage with enough space to explore, as well as toys and wheels for exercise. They like to dig, so providing digging material, such as wood chips, is beneficial.
Dental care:
Hamsters have continually growing teeth, so they need to chew regularly to wear them down. Providing chew toys and wooden blocks is essential to maintaining their dental health.
Short life cycle:
The life expectancy of a hamster is relatively short compared to other pets, generally 2 to 3 years, although this can vary depending on the species and the care provided.
Be careful with heights:
Debido a su pequeño tamaño y estructura ósea delicada, es importante tener precaución con las alturas, ya que las caídas pueden causarles lesiones.
Hibernation:
Some species of hamsters can enter a state of hibernation when temperatures drop significantly, so it is important to maintain a warm and comfortable environment for them.
Quick taming:
In general, hamsters can be quickly housebroken and accustomed to interacting with their owners, especially if handled carefully and provided with environmental enrichment.
DEGU
Degus are rodents native to Chile, known for their social nature and interesting behavior.
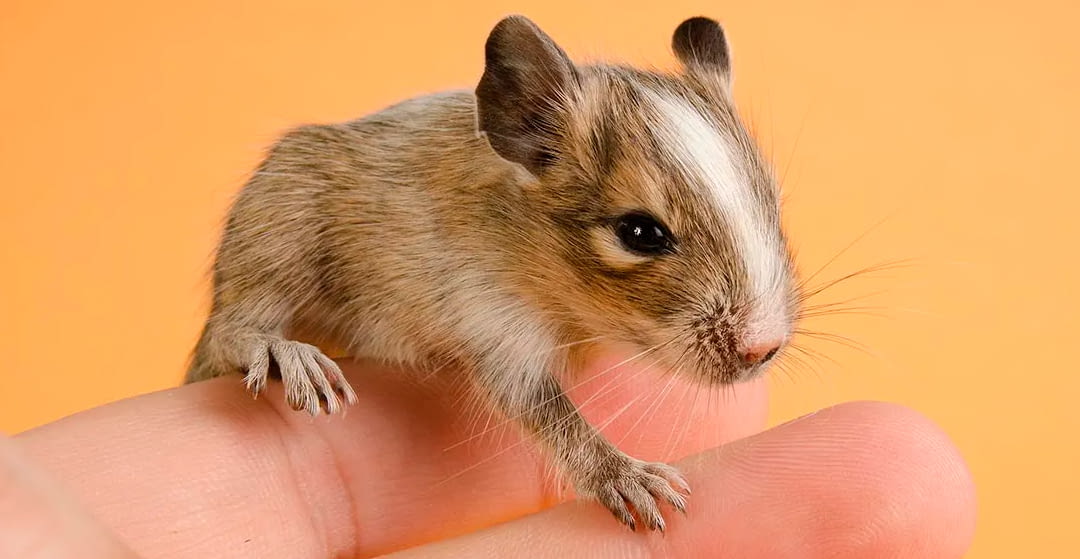

Natural habitat:
Degus are native to the central region of Chile, where they inhabit semi-arid and shrubby areas. They have adapted their behavior and physiology to a specific environment.
Appearance:
They have a thin and elongated body, with soft and dense brown or yellow fur. Its tail is long and covered with hair, and its legs are relatively short.
Social life:
Degus are extremely social animals and tend to live in family groups in the wild. It is recommended that, in captivity, they be kept in pairs or groups to meet their social needs.
Daytime activity:
Unlike some nocturnal rodents, degus are diurnal animals and are most active during the day. They enjoy exploring and climbing, so it is important to provide them with an environment enriched with toys and places to hide.
Communication:
Degus use a variety of vocalizations and body signals to communicate with each other. They can make sounds such as screeching, tapping, and growling, and they also communicate through smell and touch.
Longevity:
In captivity, degus can live 6 to 8 years if given proper care. Their longevity is influenced by factors such as diet, environment and veterinary care.
Health problems:
Degus are prone to dental problems, so it is essential to provide them with hard foods to chew and control the growth of their teeth. They may also be susceptible to diabetes and nervous system conditions.
Reproduction:
Degus are known for having a complex reproductive system. Females have a specific time during the menstrual cycle in which they can become pregnant. Gestation lasts approximately 90 days, and the pups are born fully developed.
Demanding pets:
Although degus can be charming and entertaining pets, they require specific care and commitment from their owners. Their habit of gnawing and digging means they need a sturdy, toy-enriched cage.
CHINCHILLA
Chinchillas are small rodents native to the Andes region of South America, specifically in areas such as Chile, Peru, Argentina, and Bolivia. They are known for their soft, dense fur, playful nature, and longevity.

Fur:
One of the most distinctive features of chinchillas is their extremely soft and dense fur. They have a high density of hair follicles per square centimeter, which gives them a soft, shaggy coat of fur.
Size and appearance:
Chinchillas are medium-sized rodents with compact bodies and short legs. They have large rounded ears and large eyes. Their coat can vary in colors, from standard gray to rarer variants such as beige, white or black.
Longevity:
Chinchillas have a relatively long lifespan for rodents, being able to live between 10 and 20 years if provided with proper care.
Nighttime habits:
They are nocturnal animals, meaning they are most active at night. This natural behavior must be taken into account when establishing interactions and routines with them.
Continuous denture:
Like other rodents, chinchillas have teeth that continually grow. For this reason, they need constant access to objects to gnaw on, such as blocks of wood, to wear down their teeth and prevent dental problems.
Spacious habitat:
They need a spacious habitat to jump and climb, as they are agile animals. It is recommended to provide a large, upright cage with levels and platforms to meet their exercise needs.
Powder bath:
Chinchillas do not bathe with water, but rather take dust baths to keep their fur clean and healthy. They should be provided with special chinchilla sand for this purpose.
Socialization:
Although they are social animals, not all individuals accept the company of others, so it is important to observe the behavior of chinchillas when introducing them to cage mates. It is often recommended to keep chinchillas in same-sex pairs.
Temperature and sensitivity:
Chinchillas are sensitive to high temperatures and can suffer from heat stroke. It is crucial to maintain a cool environment and provide adequate shade and ventilation.
GERBIL
Gerbils are small rodents belonging to the Muridae family, and are native to desert regions of Africa and Asia. They are sociable, active and curious animals that have become popular as pets.

Size and appearance:
Gerbils are small rodents, with slender bodies and long, muscular hind legs that allow them to jump and run quickly. They have soft fur and colors that vary depending on the species, including shades of gray, brown and white.
Social nature:
Gerbils are extremely social animals and, in the wild, live in family groups. It is recommended to keep gerbils in pairs or groups in captivity to meet their social needs.
Active behavior:
They are very active creatures and enjoy digging, digging and tunneling in their environment. Providing them with a substrate to dig, such as sand or wood chips, is essential for their well-being.
Nighttime habits:
Although they are more active during the day than some rodents, gerbils tend to be more active during nighttime hours. This should be considered when planning interactions and activities.
Longevity:
In captivity, gerbils have a life expectancy of approximately 2 to 4 years, although this can vary depending on the species and the care provided.
Quick taming:
Gerbils tend to tame quickly and can become accustomed to interacting with their owners, especially if handled carefully and provided with environmental enrichment.
Exercise wheels:
Gerbils like to run and need a lot of exercise. Providing them with an exercise wheel in their cage is essential to meet this need.
Nest construction:
They are skilled nest builders and enjoy having soft material, such as paper or hay, to build their nests.
Health problems:
Some common health concerns in gerbils include dental problems and obesity. Providing toys and chews helps keep their teeth healthy, and controlling their diet is essential to avoid obesity.
GUINEA PIG
Guinea pigs, also known as guinea pigs, are herbivorous rodents native to South America. They have been domesticated for centuries and have become popular pets due to their sociable nature and friendly behavior.

Size and appearance:
Guinea pigs are medium-sized rodents with round, compact bodies, short legs, and small ears. They have a dense, soft coat that can vary in color and texture, depending on the breed.
Social nature:
Guinea pigs are very social animals and prefer to live in groups. It is recommended to keep at least two guinea pigs together to meet their companionship needs. However, it is important to keep in mind that they should be introduced gradually to avoid conflicts.
Vocal behavior:
Guinea pigs are known for their wide repertoire of vocalizations. They may make noises such as squeaks, chirps, and growls to express various emotions, such as happiness, fear, or alertness.
Dental care:
Like other rodents, guinea pigs have teeth that grow continuously. Providing chew toys and fibrous foods helps keep their teeth in good condition.
Longevity:
In captivity, guinea pigs have a life expectancy of 5 to 7 years, although this can vary depending on the breed and the care provided.
Daytime habits:
Although they are most active during the day, guinea pigs can also be active at night. Providing a quiet, dark environment for rest is important.
Coat care:
Guinea pigs require regular coat care. Depending on coat length, some breeds will need regular brushing to prevent tangles and skin problems.
Spacious habitat:
A spacious cage is recommended to allow guinea pigs to move and explore. Make sure the cage has enough ventilation and is equipped with toys and places to hide.
Affectionate and affectionate:
Guinea pigs are known for being loving and affectionate pets. Many of them enjoy interacting with their owners and can be trained to recognize their names and respond to certain commands.