Many pet owners consider rodents to be excellent companions. There are many different species and for all kinds of living spaces, from large to small.
However, it is important to take into account that the coexistence of rodents in the same space can be complicated and is not always successful, since some of them are territorial and can have conflicts. Here are some species that often get along when kept together:
SAME SPECIES
House Mice (Mus musculus): House mice tend to be social and can live together in groups if introduced early. Make sure you give them enough space and resources to avoid conflict.
Dwarf Hamsters (Phodopus spp.): Dwarf hamsters, such as the Russian hamster and Chinese hamster, can often live in pairs or small groups if introduced from an early age. However, it is essential to watch for any signs of aggression and be prepared to separate them if necessary.
Gerbil Mice (Meriones unguiculatus): Gerbil mice are social and can generally live in groups if they are of the same sex and are introduced at the same time. It's important to make sure you have enough space and enrichment to keep them occupied.
Guinea Pigs (Cavia porcellus): Although not technically rodents, guinea pigs are social animals and often enjoy the company of others of their kind. It is best to keep them in same-sex groups to avoid unwanted breeding.
Domestic Rats (Rattus norvegicus): Domestic rats are very social and tend to get along in groups. As with mice, it is best to introduce them young and provide them with plenty of space and stimulation.
It is important to thoroughly research the specific needs of each species and be prepared to separate animals if conflicts arise. Also, keep in mind that even species that are generally social can have individual differences in terms of temperament, so monitoring their behavior and making sure all animals are healthy and happy is essential.
It is always advisable to consult with a small animal veterinarian before introducing any new species into the home.

DIFFERENT SPECIES
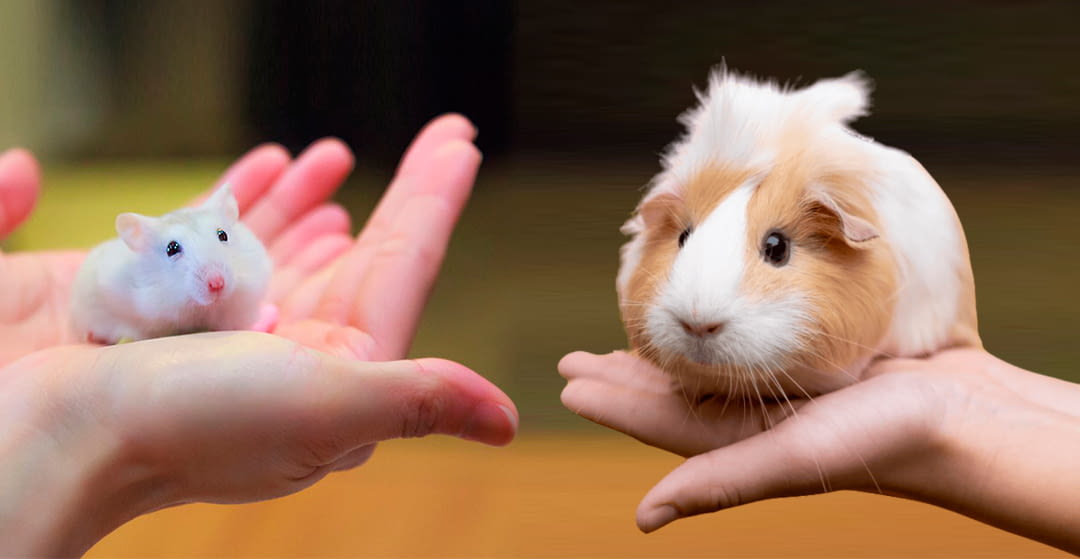
Introducing different species of rodents into the same space can be risky and is not recommended in most cases. Different species of rodents have different behaviors, needs, and temperaments, which could lead to conflict, stress, and even serious injury.
Here we show you some reasons why it is not advisable to mix different species of rodents:
Competition for resources: Different species of rodents may compete for food, water, space, and other resources in the shared environment. This can lead to aggression and stress.
Differences in behavior: Rodent species have different natural behaviors that may not be compatible. Some species can be more territorial or aggressive than others, which can result in fighting.
Differences in size and strength: Some species of rodents are much larger or stronger than others. This could lead to dangerous situations where a larger species hurts or kills a smaller one.
Differences in communication: Rodents use specific communication signals between individuals of the same species. Introducing a different species can cause misunderstandings and conflicts due to differences in communication.
Diseases and parasites: Different species of rodents can carry different diseases and parasites. By mixing species, the risk of disease transmission between them can be increased.
In summary, although it may seem tempting to keep a variety of rodent species in one space, it is actually safer and healthier to keep different species in separate environments.